SDT is a computer controlled spinning drop tensiometer
for measuring interfacial tension between two immiscible liquids. Its unique
built-in oven capable of creating a temperature environment of up to 300ºC
makes it the only tensiometer in the market that handles polymer melts.
Features of SDT include:
- 0.0001 mN/M ~ 500 mN/M• measuring range;
- 12.7mm testing tube, good for crude oil, surfactant solutions;
- Built-in oven for temperatures up to 300º C;
- Embeded calibration node, no need for optical correction;
- Direct drive motor providing vibration-free operation even at 15,00 rpm;
- Controllers with digital displays;
- Computer controlled image acquisition and data analysis;
- Dynamic measurement for relaxation curve.
SDT was first developed by
Daniel D Joseph and
his associates for Hoechst-Celanese
Corporation for its polymer research. Many improvements have been made over
the years. The large RPM range of SDT allows one to measure both small
and large interfacial tensions. The evolution to equilibrium in very viscous
liquids can be speeded up by controlled centripetal forces which replace
gravity in other types of tensiometers. A high temperature application of
STD to the study of the effect of copolymer on the tension between molten
polymers is described in
C. Verdier, H. Vinagre, M. Piau and D. Joseph (2000) High
Temperature Interfacial tension measurements of PA6/PP Interfaces
Compatibilized with Copolymers using a spinning drop tensiometerto appear
in Polymer Communications; (retrieve 125k file in Adobe Acrobat PDF
format).
See also the web page of Claude Verdier, University of Grenoble, at
http://rheologie.ujf-grenoble.fr/verdier/.
A comparative study of the absorption of surfactants at a bitumen/H2O and bitumen/D2O interface is
presented in
M. Di Lorenzo (PDVSA-Intevep), H. Vinagre, and D.
Joseph, (2000) Adsorption of Intan-100 at the Bitumen/Aqueous Solution
Interface Studied by Spinning Drop Tensiometry to appear in Colloids and
Surfaces; (retrieve 170k file in Acrobat
PDF format)
SDT was first described in the patent
D.D. Joseph, D.A. Hultman (1992) Spinning Drop
Tensioextensiometer, United States Patent, Patent Number 5,150,607.
and more completely in the paper
D.D. Joseph, M.S. Arney, G. Gillberg, H. Hu, D.A. Hultman, C. Verdier,
and H. Vinagre (1992) A spinning drop tensioextensiometer, J. of
Rheology, 63(4).
Most measurements of interfacial tension
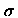 use Vonnegut's formula use Vonnegut's formula
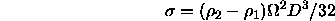
where
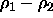 is the density difference and
is the density difference and
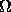 is the
angular velocity of the drop. This formula is accurate when the drop diameter
D is four times shorter than the drop length L; when
L/D 4 the formula can be corrected using table 4 in the paper is the
angular velocity of the drop. This formula is accurate when the drop diameter
D is four times shorter than the drop length L; when
L/D 4 the formula can be corrected using table 4 in the paper
P. Than, L Preziosi, D.D. Joseph and M.S. Arney, (1988)
Measurement of Interfacial Tension Between Immiscible Liquids with the
Spinning rod Tensiometer, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 124, 552-559.
which is embedded in SDT software. Other references:
D.D. Joseph, M.S. Arney and G. Ma, (1992) Upper and lower bounds
for interfacial tension using spinning drop devices J. Colloid Interface
Sci., 148, 291.
D.D. Joseph, L. Preziosi, (1987) Stability of rigid motions and
coating films in bicomponent flows of immiscible liquids J. Fluid Mech.
185, 323-351.
H. Princen, I. Zia and S.G. Mason(1967) Measurement of
Interfacial Tension from the Shape of the Rotating DropJ. Colloid Interface
Sci., 23, 99-107.
|

